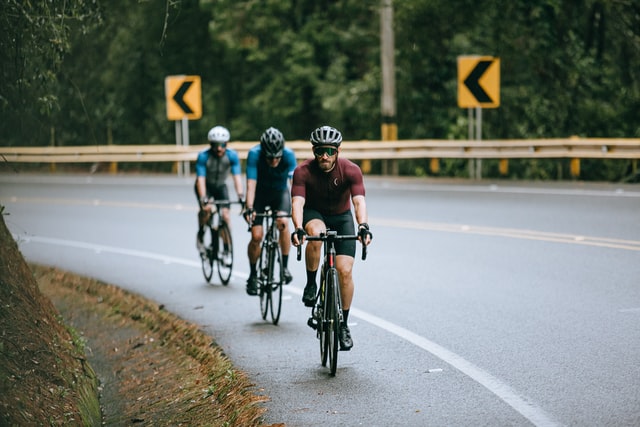
Whilst you may have come across the term sports nutrition, you may not fully understand what it entails. Growing in popularity, sports nutrition is the study and implementation of a personalised health plan designed to increase athletic performance. In this article, Human Health Hub explores the three principles of sports nutrition and outlines how we can put them into practice.
So, what are the three principles of sports nutrition? The three principles that make up sports nutrition are:
- Fuelling (nutrition)
- Hydration
- Recovery
Keep reading to learn more about these principles and the many benefits of taking part in a sports nutrition program.
3 Principles of Sports Nutrition
Sports nutrition refers to nutritional strategies that are put in place to aid athletic performance. This can help athletes prepare and recover from training or competition. The three principles of sport nutrition include fuel or nutrition, hydration, and recovery. These are absolutely key for performance. Like putting petrol in a car, having the right fuel is vital. However, it’s important to remember that each principle varies depending on the individual’s unique requirements (type of sport and performance level).
Here is everything you need to know about the three basic components of sports nutrition:
Fuelling
Fuelling involves providing your body with the right kinds of foods to enhance your stamina, strength and clarity. You’ll want to aim for a variety of whole grains, vegetables, fruits, lean protein sources and healthy fats.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates play a key role in the diet of any athlete. This is because carbohydrates are a major muscle fuel source. It doesn’t matter how much muscle you build, if your body is not getting enough carbohydrates, it won’t be able to sustain itself during exercise. The type of sport and frequency will determine the volume of carbohydrate intake. A common misconception surrounding carbohydrates is that they are wholly bad for us, however, this is certainly not the case. It all depends on what kinds of carbohydrates you are consuming. It is about working out how much you deserve and need in your food regime. Body carbohydrate stores provide an important fuel source for the brain and muscle during exercise and are manipulated by exercise and dietary intake. Our recommendations for carbohydrate intake typically range from 3-10 g/kg BW/d and up to 12 g/kg BW/d for extreme and prolonged activities. These guidelines also depend on the:
- Fuel demands of training or competition
- Balance between performance and adaptation goals
- Athlete’s total energy requirements and body composition goals
Targets should be individualised to the athlete’s event and periodised over the week. Training cycles of the seasonal calendar should be determined according to changes in exercise volume and the importance of high carbohydrate availability for different exercise sessions.
Below, we outline the five factors that regulate your carbohydrate intake:
- Training volume and Intensity,
- Total Sum of body fat percentage,
- Total Sum of muscle mass,
- Subscapular and supra-iliac skinfold.
- Stress levels (Physical and mental)
When it comes to eating carbohydrates, it is all about management. For example, having carbohydrates too early will slow down or even reverse your progress. However, not having enough will lead you to being lean but small. Balance is absolutely crucial.
Protein
Protein is important for any food regime. It is essential for many functions of the body, including recovery from training and building muscle. How much protein we require will depend on many factors, but our guideline is 1.6g to 4 kg per kg bodyweight.
For most people, protein is supplied through meat, poultry and fish. However, many sportspeople are now turning to plant-based sources for their protein. The downside to plant-based protein is that it may not deliver enough calcium or iron. This is where it may be helpful to use a supplement. On the plus side, plant-based protein is by definition, lean. No matter what type of protein you are consuming, the key is to make sure that it is high-quality.
Fibre
If you are following a healthy food regime, chances are, you’ll be consuming the fibre you need as a natural outcome of that. For example, complex carbohydrates tend to be from whole grains, which are a fantastic source of fibre. In sports nutrition, fibre is important because it is essential for a healthy digestive system. Generally, if you lack fibre, you’re unlikely to get the full benefit of whatever else you are eating.
Hydration
In principle, water is the most effective form of hydration. The goal of drinking during exercise is to address sweat losses which occur to assist thermoregulation. Individualised fluid plans should be developed to use the opportunities to drink during a workout or competitive event to replace as much of the sweat loss as is practical; neither drinking in excess of sweat rate nor allowing dehydration to reach problematic levels. After exercise, the athlete should restore fluid balance by drinking a volume of fluid that is equivalent to 125-150% of the remaining fluid deficit (e.g. 1.25-1.5 L fluid for every 1 kg BW lost).
For the most part, fizzy drinks and alcohol are best avoided or consumed in moderation. The only exception is proper sports drinks, like hydration and electrolyte drink mixes (not energy drinks such as Lucozade Sport). These can be a convenient way to rehydrate and replace key nutrients after intense exercise. It is important to make sure that you are buying a high-quality drink created for athletes. Remember, during exercise, you lose fluid and electrolytes as you sweat. If you don’t replenish this fluid and sodium, you can become dehydrated. Dehydration can increase the perception of effort and impair exercise performance, which is why it is so important to consume an appropriate fluid intake before, during and after exercise.
We recommend that you kickstart your day with a glass of water containing lime (lemon) and salt as it boosts energy, immunity, gut health and decreases stomach fat.
Top tip – A good way to monitor your hydration levels is to pinch your skin to test its responsiveness. Basically, the quicker your skin bounces back, the better hydrated you are.
Recovery
When your muscles have worked hard, it’s important to promote their recovery. This is the time to consume simple carbohydrates and easily digestible protein. It can, however, be a lot more convenient to use post-workout supplements. These high-quality post-workout supplements are made to give your body exactly what it needs to recover after a workout. What’s more, they’re formulated to fit modern lifestyles. For example, putting together a post-workout recovery drink can be done in moments. These supplements can also be easier on your stomach than regular food. Often, after a workout, you’ll crave nourishment but not want to eat solid food. A post-workout drink can be the perfect solution to this problem.
If you’re eager to learn more about how strength training affects nutritional requirements, take a look at our recent article at Human Performance Hub.
Other Factors To Take Into Consideration
On top of the three principles we have already discussed, here are some other factors to bear in mind when thinking about sports nutrition:
- Training intensity & volume
- Total body fat percentage
- Total muscle mass
- Physical and mental stress
At Human Health Hub, we use a combination of skin fold analysis, continuous glucose monitoring and blood test results to determine your body fat percentage and total muscle mass.
How Can a Sports Nutritionist Help?
Sports nutritionists are responsible for implementing science-based nutrition protocols for athletes and people that are enthusiastic about training. Their role is to educate athletes on all aspects of nutrition related to sports performance, including taking in the right amount of food, nutrients, hydration and supplementation when needed.
A day in the life of a sports nutritionist will often include the following:
- Meeting with clients one to one to formulate individual plans
- Strategising with team management
- Being present during pre and post-training meals to help guide athletes’ food choices
- Ensuring clients are well nourished to perform at their highest level
Here at Human Health Hub, we’re fitness and nutrition consultants who work with clients towards a common goal of improving overall health, wellbeing and quality of life. We’ll provide superior support, resources, techniques and a bespoke nutrition plan so that clients can reach their health, fitness and performance goals.
What Are The Benefits of Sports Nutrition Coaching
Nutrition coaching is so much more than generally improving an individual’s food regime or calorie counting. Instead, it considers the fact that everyone’s nutritional needs differ based on their health, lifestyle and performance goals.
Some of the main benefits include:
- Support and advice tailored to your goals
- Better overall health
- Enhanced physical condition
- Boosts athletic performance
- Mood improvements
Supplements For Sports Nutrition
In general, whole foods should make up the majority of an individual’s food regime. That being said, considering that athletes often have greater nutritional needs, supplementation can be used to fill in any gaps in the plan.
Here are some of the top science-backed supplements often recommended by sports nutritionists:
Protein Powders
Protein powders are isolated forms of various proteins, such as whey, egg white, pea, brown rice and soy. They typically contain around 10-25g of protein per scoop, making it easy to consume a solid dose of protein. Research suggests that consuming a protein supplement around training can help promote recovery and aid in increases in lean body mass.
Carbohydrate Gels & Powders
Carbohydrate supplements may help sustain your energy levels, especially if you engage in endurance sports lasting longer than 1 hour. These concentrated forms of carbohydrate usually provide about 25g of simple carbohydrate per serving. They either come in gel or power form.
Vitamins & Minerals
Many athletes choose to take high quality vitamins that contain all the basic vitamins and minerals to make up for any potential gaps in their food plan. This is a good idea for most people, as the potential benefits of supplementing with a multivitamin outweigh the risks. One vitamin in particular that athletes often supplement with is Vitamin D, especially during winter in areas with less sun exposure.
Fish Oil
Supplementing with omega-3 fats such as fish oil may improve sports performance and recovery from intense exercise. You can get omega-3s from your diet by eating foods such as fatty fish, flax, chia seeds, nuts and soybeans. If however, you don’t often include these foods in your diet, supplementing with fish oil may be a good idea.
Plant-based omega-3 supplements are also available for those who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Creatine
Creatine is a compound your body produces from amino acids. It’s also found in small amounts in meat and fish. It aids in energy production during short, high intensity activities. Supplementing daily with 5 g of creatine monohydrate, the most common form, has been shown to improve power and strength output during resistance training, which can carry over to sports performance.
Take a look at our ATP Lab Myoprime Creatine Pre Workout supplement at Human Performance Hub to find out more.
What Is The Future of Sports Nutrition?
There is huge potential in the future of sports nutrition, as it promises to revolutionise the way athletes fuel their performance and recovery. With advancements in personalised nutrition, function foods and sustainable practices, athletes can expect tailored strategies that optimise their potential. By embracing technology, prioritising gut health and collaborating with sports science, sports nutrition will pave the way for evidence-based nutrition plans designed to unleash peak athletic performance. As this field continues to evolve, athletes and sports nutrition professionals can look forward to a future where nutrition plays a vital role in unlocking athletic excellence.
Sports Nutrition Consultation At Human Health Hub
Now that you’re fully up to speed with the importance of sports nutrition, why not take a look at Human Health Hub’s sports nutrition program. Our sports nutrition consultation service is a branch of functional nutrition that aims to help athletes achieve sporting performance by optimising their food plan and supplementation to suit individual goals.
Our functional medicine practitioner, Roan Heming will teach you how nutrition impacts performance, recovery and general health. You’ll also learn how various foods and supplements can impact different areas of performance, whether that be speed, strength, stamina or accuracy. So, what are you waiting for? Book your free discovery call today to find out how we can help you reach your health and fitness goals.